Tags
Results for: Vector-borne Disease
-
Article ItemCategory: impact Risks posed to humans by rare but deadly mosquito-borne disease, explained by veterinary expert , article
Sierra Guynn, a clinical assistant professor with the Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine, discusses the history and public health risks of eastern equine encephalitis (EEE), a rare but potentially deadly mosquito-borne disease that can spread between people and animals.
Date: Aug 30, 2024 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Luis Escobar receives NIH award to study rabies transmission from wildlife to humans , article
Escobar will study vampire bats in Latin America to learn more about the spillover of a wildlife disease that can severely impact human health: rabies.
Date: Sep 25, 2023 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Luis Escobar receives NSF CAREER award to study disease transmission among wildlife and across geographic scales , article
With the National Science Foundation award, Escobar will research the disease ecology and biogeography of hantavirus to better understand disease transmission between species and to humans.
Date: Feb 27, 2023 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Virginia Tech researchers find potential roadmap to removing mosquitoes’ ability to transmit malaria , article
College of Agriculture and Life Sciences researchers are the first to study three-dimensional genome organization – particularly how the genome can be folded and still accessed by enzymes for transcription purposes – in mosquitoes.
Date: Jun 10, 2022 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Researchers receive $1.75 million grant to study host variation , article
Disease outbreaks and evolution are hard to predict. Researchers at Virginia Tech and three other institutions are studying immunity variation to get a better grasp on this phenomenon.
Date: Sep 27, 2021 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Breaking the deadly cycle: Drug researchers tackle the malaria parasite at multiple life stages , article
Researchers have received a $3.7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to begin further testing of two inexpensive and effective antimalarial drug candidates that can kill Plasmodium parasites at three stages of their development.
Date: Aug 30, 2021 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Revolutionary mosquito researchers receive $2.7 million grant , article
Funded by a $2.7 million grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, researchers at Virginia Tech are now investigating how mosquitoes adjust their smelling rhythms in response to changes in our own daily activity.
Date: Jul 15, 2021 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Virginia Tech researchers identify a missing piece of the Lyme disease puzzle , article
Virginia Tech Assistant Professor Brandon Jutras and his lab have continued to tackle the Lyme disease epidemic over the past year, and they have recently identified another missing piece of the Lyme disease puzzle.
Date: May 13, 2021 - -
Article ItemCategory: academics Mathematics’ Lauren Childs helps address the complex problems of malaria , article
Childs recently co-authored a report with a team from Harvard University on the role of natural mosquito behavior on transmission of a disease that threatens half the world’s population.
Date: Feb 23, 2021 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Tick maps: Merging epidemiological data with technology , article
Professor Korine Kolivras applies geographical expertise and geospatial tools to study the spread of Lyme disease in the southeastern U.S.
Date: Nov 11, 2020 - -
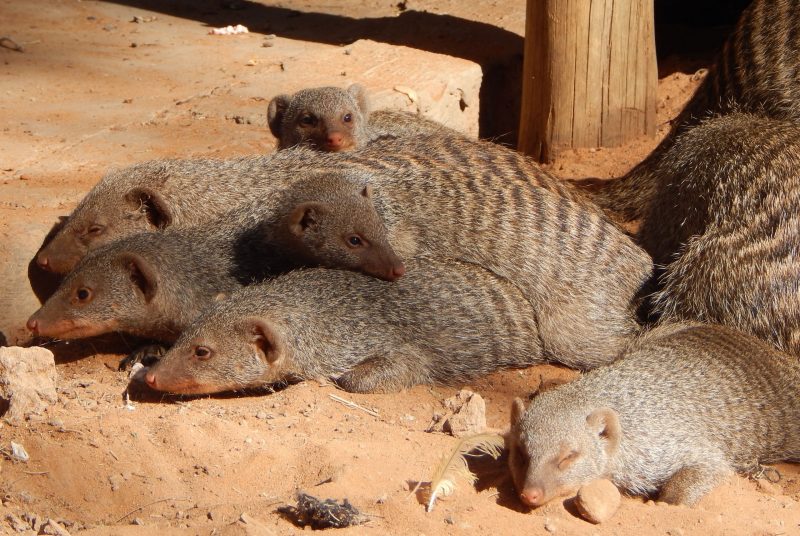
Article ItemCategory: research Banded mongoose study reveals how behavior and landscape interactions influence the spread of infectious disease , article
Researchers observed banded mongoose in several different environments in Botswana, gaining insight into the spread of a novel tuberculosis pathogen that is transmitted through olfactory communication behaviors.
Date: Mar 12, 2020 - -
Article ItemCategory: academics Virginia Tech researchers join global effort to develop a new vector control strategy to prevent malaria , article
Malaria, according to the U.S. Agency for International Development, continues to be a leading cause of illness and death worldwide. Despite extensive work that has produced widespread improvements in fighting the spread of the disease, global efforts have hit a plateau.
Date: Apr 11, 2019 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Virginia Tech researcher: To slow malaria, cure mosquitoes with drug-treated bed nets , article
Virginia Tech's Lauren Childs is part of a research group showing that using the anti-malaria drug atovaquone to coat mosquito bed nets makes mosquitoes ingest and absorb the drug.
Date: Mar 08, 2019 - -
Article ItemCategory: academics Statistics’ Leah Johnson seeks to improve quantitative models for fighting diseases in humans, trees , article
Johnson, an assistant professor in the College of Science, will use a $700,000 National Science Foundation CAREER grant to help fight deadly diseases by using mathematical and statistical modeling.
Date: Apr 10, 2018 - -
Article ItemCategory: campus experience Mosquitoes remember human smells, but also swats, Virginia Tech researchers find , article
A study shows that mosquitoes can rapidly learn and remember the smells of hosts and that dopamine is a key mediator of this process.
Date: Jan 25, 2018 - -
Article ItemCategory: research Mathematical model helps target malaria-carrying mosquitos , article
Lauren M. Childs of the College of Science has helped build a mathematical model used in the development of a new compound that targets mosquitoes known to carry malaria.
Date: Jan 18, 2017 - -
Article ItemCategory: campus experience Fralin Life Science Institute honors benefactors at 20-year anniversary celebration , article
Attendees learned about the institute’s signature research areas: the Vector-borne Disease Research Group, Global Change Center, and the planned Center for Transformative Research on Health Behaviors.
Date: Dec 01, 2016 - -
Article ItemCategory: campus experience Virginia Tech research team's discovery aims to reduce deaths caused by African sleeping sickness , article
The breakthrough came when the team, led by Fralin Life Science Institute researcher Zac Mackey, discovered that the parasite Trypanosoma brucei uses a distinct method to perform a biochemical process known as phosphorylation.
Date: Sep 23, 2016 - -
Article ItemCategory: academics Fralin researcher finds gene that reduces female mosquitoes , article
Males are preferred because they do not bite. Female mosquitoes bite to get blood for egg production and are the prime carriers of the pathogens that cause malaria, Zika, and dengue fever.
Date: Sep 21, 2016 - -
Article ItemCategory: campus experience Virginia Cooperative Extension offers tips for controlling mosquitoes , article
Eric Day, manager of the Virginia Tech Insect Identification Lab, reminds residents that understanding basic mosquito habits and taking steps to disrupt their lifecycles can reduce the threat significantly.
Date: Jul 05, 2016 -
Page 1 of 3 | 45 Results