Virginia Tech research magazine reports on saving wildlife, recovering coal from slurry ponds, treating brain tumors, who is running the country

The winter issue of Virginia Tech Research reports on inventions to advance human health and energy resources.
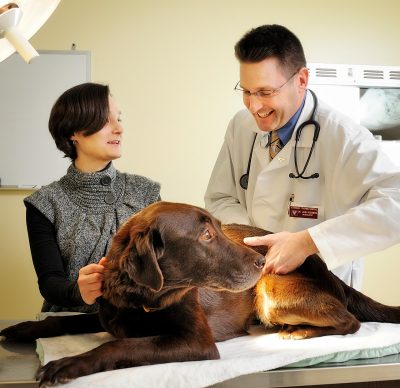
Physicians are watching with interest as veterinarians use a new treatment developed by biomedical engineers to threat tumors in dogs. It turns out that the most deadly of brain tumors happen in people and pooches. The new treatment, non-thermal irreversible electroporation, delivers short electric pulses to cancer cells.
Meanwhile, another invention has made it possible to extract and dry super-fine coal that has previously had to be discarded. Slurry ponds have now become an energy resource.
A series of new processes is making it possible to convert dry biomass into hydrogen at point of use, meaning the volatile gas would not have to be moved or stored. When a novel mixture of enzymes and water are added to plant sugars, the enzymes create hydrogen gas that can power a fuel cell.
Wildlife scientists are discovering how the red knot, a bird that migrates from South America to the Arctic with only one stopover, is able to survive despite loss of much of their food supply. Red knots thrived until they had to share the horseshoe crab increasingly with humans. Now birds survive on donax, a hard shell crab – but have to eat more of them.
Human-animal interactions also present challenges in Africa. Tourists love elephants, but the huge animals can wreck a crop. Close encounters between humans, domestic animals, and wildlife also present disease challenges, such as a newly discovered type of tuberculosis being seen in mongoose. A one-health attitude is helping local communities develop strategies to manage the human-animal interface.
Two hundred years ago, an 8.0 earthquake changed the land and rivers over hundreds of miles and created new lakes in mid-America. It could happen again. A Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)-funded study has analyzed the impact of a major earthquake of the 150-mile-long New Madrid Seismic Zone. More than 7 million people in six states would be affected.
The study of the impact of a New Madrid Seismic Zone quake is a resource for decision makers and responders. Hopefully, the appropriate federal agencies will have time to read it and plan, and not be distracted by a lack of leadership. A study of political appointees reveals, on one hand, that they tend to be good public servants – but, on the other hand, there are many many vacancies, or ghosts, in key positions.
Dedicated to its motto, Ut Prosim (That I May Serve), Virginia Tech takes a hands-on, engaging approach to education, preparing scholars to be leaders in their fields and communities. As the commonwealth’s most comprehensive university and its leading research institution, Virginia Tech offers 240 undergraduate and graduate degree programs to more than 31,000 students and manages a research portfolio of $513 million. The university fulfills its land-grant mission of transforming knowledge to practice through technological leadership and by fueling economic growth and job creation locally, regionally, and across Virginia.