U.S. Marine Corps to use autonomous vehicles built by Virginia Tech engineering students
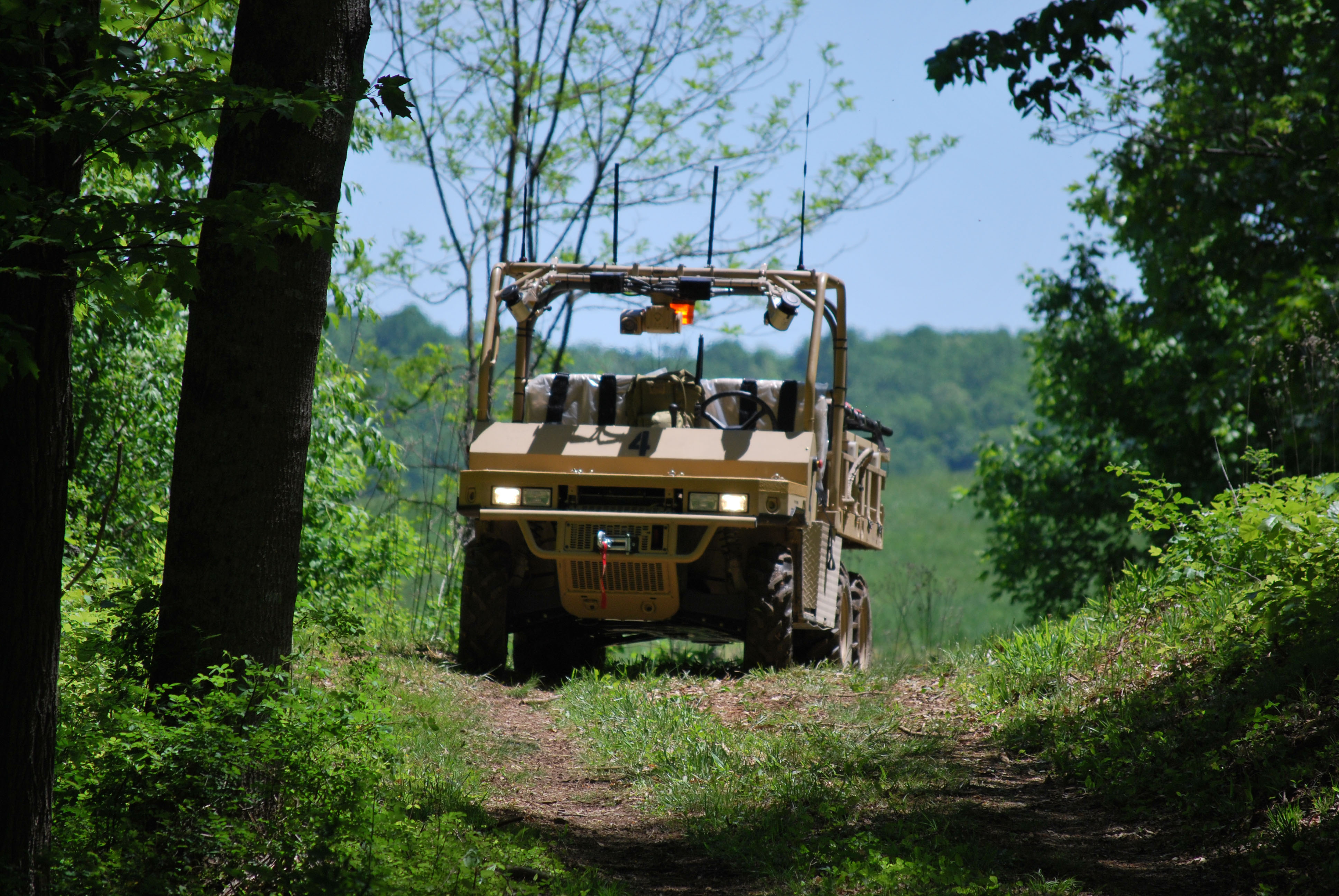

Four unmanned autonomous vehicles designed and built by a team of engineering students at Virginia Tech using the TORC Robotic Building Blocks product line, are headed to Hawaii to participate in the 2010 Rim of the Pacific (RIMPAC) war games in July.
Fourteen nations, 34 ships, five submarines, over 100 aircraft and 20,000 personnel will participate in the biennial RIMPAC exercise June 23 through Aug. 1.
The U.S. Marine Corps Warfighting Laboratory worked closely with Virginia Tech and TORC in the creation of the four Ground Unmanned Support Surrogates (GUSS) that will be used for their ability to support a platoon of U.S. Marines.
The unmanned vehicles can carry up to 1,800 pounds and can move at the speed of a troop on foot, or about five miles per hour. The vehicles are designed to re-supply troops, to reduce the actual loads manually carried by Marines, and to provide an immediate means for the evacuation of any casualties in combat. A Marine unit will operate GUSS during the Naval Laboratory’s enhanced company operations experimentation that coincides with RIMPAC.
Virginia Tech and TORC, a company founded by alumni of the university’s robotics program, share a very successful track record on their collaborations. Together, they developed autonomous vehicles for the Urban Challenge competition sponsored by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in 2006 and in 2007.
“The focus of the collaborations is to leverage the research capabilities of the university with the commercialization capabilities of a small business,” said Al Wicks, professor of mechanical engineering (ME) at Virginia Tech and faculty advisor to the team.
They took home third place honors in 2007 when their vehicle completed DARPA’s 60-mile course in less than six hours, with no human intervention allowed past the starting line.
The four GUSS vehicles headed to Hawaii are an outgrowth of the technology developed for these DARPA competitions, Wicks said. The sensors have been greatly improved, as well as the perception, planning, and control algorithms to navigate complex environments.
The Urban Challenge featured a cooperative environment with well-defined roads for the competition. When the GUSS vehicles are used by the Marine Corps in Hawaii, they will be “off-road and not in a cooperative environment,” Wicks said. “This is a big step forward in autonomous vehicles.”
Michael Fleming, a Virginia Tech ME graduate and the founder and chief executive officer of TORC, explained the team synergism, saying “I believe our team of government, academia, and industry all working together has provided the Marine Corps with a well-balanced solution.”
As an example, existing algorithms developed by students under previous TORC/Virginia Tech partnerships, were used to create a customized version of the TORC AutonoNav (autonomous navigation system) product to provide the advanced off-road tactical behaviors required to meet the needs of the Marine Corps Warfighting Lab.
The rapid development and experimentation on the GUSS project was made possible through the use of TORC’s Robotic Building Blocks product line, said David Cutter, marketing manager at TORC. This enabled Virginia Tech engineers to leverage off-the-shelf technologies and focus on system integration challenges. The entire development process was completed in less than a year, with the first prototype delivered for testing in six months. The additional three vehicles were produced in the next five months to be shipped to the RIMPAC exercises.
The WaySight, developed by TORC, is the primary operator interface for controlling the GUSS vehicles. Using the 1-pound handheld unit, Marines are able to command the unmanned vehicles in several modes depending on the mission. The operator may use the WaySight to rapidly plan a new path, take remote control of the vehicle, or direct it to follow at a safe distance with the autonomous navigation system taking over.
The project is part of a five-year contract between the Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren Division and Virginia Tech that is supporting a number of different projects. The contract is an on-going agreement between Dahlgren and Virginia Tech’s Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science (ICTAS) to foster innovative research.
The mechanical engineering seniors who participated in the project and their hometowns are: Patrick Currier of Murfreesboro, Tenn.; Phillip Tweedy of Lynchburg, Va.; James May of Atlanta, Ga., Jason Doyle of Blue Ridge, Va., and Everett Braden of Roanoke, Va.
The College of Engineering at Virginia Tech is internationally recognized for its excellence in 14 engineering disciplines and computer science. The college's 6,000 undergraduates benefit from an innovative curriculum that provides a "hands-on, minds-on" approach to engineering education, complementing classroom instruction with two unique design-and-build facilities and a strong Cooperative Education Program. With more than 50 research centers and numerous laboratories, the college offers its 2,000 graduate students opportunities in advanced fields of study such as biomedical engineering, state-of-the-art microelectronics, and nanotechnology. Virginia Tech, the most comprehensive university in Virginia, is dedicated to quality, innovation, and results to the commonwealth, the nation, and the world.